Polynomial Counter
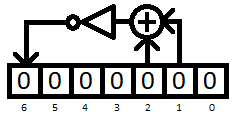
The polynomial counter is a Fibonacci linear-feedback shift register that serves as the less significant 7 bits of the CIC's program counter. Its taps are located at bits 1 and 2, which are XOR'd together, inverted, and fed back into bit 6. Unlike most program counters which increment by the size of an instruction, the polynomial counter is stepped according to a special formula:
void CIC::poly_inc()
{
// bit 0 is output-only
bool bit1 = pc & 0x01;
bool bit2 = pc & 0x02;
bool bits12_xor = bit1 ^ bit2;
bool bits12_xnor = !bits12_xor;
pc = (pc & 0x380) + (bits12_xnor * 0x40) + (pc & 0x7E) / 2;
}
Presumably, it takes fewer transistors to step this way than a standard ripple carry incrementor. The sum-of-three-terms formula in the pc assignment statement above is equivalent to a bit-shift and bitwise or, which better illuminates the fact that "polynomial" is just a fancy way to describe the linear-feedback:
pc = (pc >> 1) | (bits12_xnor * 0x40);
If the polynomial counter begins at 00h and runs a straightforward control flow graph (e.g. no jumps/branches/calls/returns), this is the sequence it will count through:
00 40 60 70 78 7c 7e 3f 5f 6f 77 7b 7d 3e 1f 4f 67 73 79 3c 5e 2f 57 6b 75 3a 1d 0e 07 43 61 30 58 6c 76 3b 5d 2e 17 4b 65 32 19 0c 46 23 51 28 54 6a 35 1a 0d 06 03 41 20 50 68 74 7a 3d 1e 0f 47 63 71 38 5c 6e 37 5b 6d 36 1b 4d 26 13 49 24 52 29 14 4a 25 12 09 04 42 21 10 48 64 72 39 1c 4e 27 53 69 34 5a 2d 16 0b 45 22 11 08 44 62 31 18 4c 66 33 59 2c 56 2b 55 2a 15 0a 05 02 01
before cycling back to 00h.
Note that 7Fh is unique in that it is the only 7-bit value that does not appear in this sequence. That is because 7Fh is idempotent - if the counter ever reaches 7Fh somehow (like through a JMP) then trying to step it will only result in it staying at 7F, so the CIC hangs at that address.
Sources: