XBA: Difference between revisions
(XBA only way to access B byte) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
|[[Carry Flag|C]] | |[[Carry Flag|C]] | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
| | |N | ||
|. | |. | ||
|. | |. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
|. | |. | ||
|. | |. | ||
| | |Z | ||
|. | |. | ||
|} | |} | ||
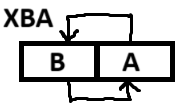
'''XBA''' is | '''XBA''' is a [[65c816]] instruction that exchanges the high byte (B) and low byte (typically called A) of the [[C accumulator]]. It works even in [[6502 emulation mode]]. In [[65816 native mode]], its standard mnemonic is still "XBA" even when the accumulator is 16-bits wide. An alternative mnemonic is "SWA." | ||
XBA can be used to convert [[big endian]] data to [[little endian]] and vice versa. XBA appears to be the only way to access the high B byte when the [[M flag]] is set. | |||
The [[negative flag]] will match the most significant bit of the new low byte (A) of the accumulator. | |||
The [[zero flag]] will be set if and only if the new low byte (A) of the accumulator is zero, otherwise it is cleared. | |||
==== Syntax ==== | |||
<pre> | |||
XBA | |||
SWA | |||
</pre> | |||
Even though the hidden B byte is colloquially considered to be second accumulator, XBA still isn't considered to use [[accumulator addressing]]. | |||
[[File:xba.png]] | |||
=== See Also === | === See Also === | ||
| Line 43: | Line 58: | ||
=== External Links === | === External Links === | ||
* [[Eyes & Lichty]] | * [[Eyes & Lichty]], [https://archive.org/details/0893037893ProgrammingThe65816/page/524 page 524] on XBA | ||
* [[Labiak]] | * [[Labiak]], [https://archive.org/details/Programming_the_65816/page/n214 page 204] on XBA | ||
* snes9x implementation of XBA: https://github.com/snes9xgit/snes9x/blob/master/cpuops.cpp#L3261 | * snes9x implementation of XBA: https://github.com/snes9xgit/snes9x/blob/master/cpuops.cpp#L3261 | ||
* undisbeliever on XBA: https://undisbeliever.net/snesdev/65816-opcodes.html#xba-exchange-the-b-and-a-accumulators | * undisbeliever on XBA: https://undisbeliever.net/snesdev/65816-opcodes.html#xba-exchange-the-b-and-a-accumulators | ||
* Clark, Bruce. http://www.6502.org/tutorials/65c816opcodes.html#6.10.3 | |||
[[Category:ASM]] | [[Category:ASM]] | ||
| Line 53: | Line 69: | ||
[[Category:One-byte Instructions]] | [[Category:One-byte Instructions]] | ||
[[Category:Implied Instructions]] | [[Category:Implied Instructions]] | ||
[[Category:Three-cycle Instructions]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:12, 11 August 2024
| Basic Info | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Addressing Mode | Opcode | Length | Speed | ||||
| Implied (type 1) | EB | 1 byte | 3 cycles | ||||
| Flags Affected | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | V | M | X | D | I | Z | C |
| N | . | . | . | . | . | Z | . |
XBA is a 65c816 instruction that exchanges the high byte (B) and low byte (typically called A) of the C accumulator. It works even in 6502 emulation mode. In 65816 native mode, its standard mnemonic is still "XBA" even when the accumulator is 16-bits wide. An alternative mnemonic is "SWA."
XBA can be used to convert big endian data to little endian and vice versa. XBA appears to be the only way to access the high B byte when the M flag is set.
The negative flag will match the most significant bit of the new low byte (A) of the accumulator. The zero flag will be set if and only if the new low byte (A) of the accumulator is zero, otherwise it is cleared.
Syntax
XBA SWA
Even though the hidden B byte is colloquially considered to be second accumulator, XBA still isn't considered to use accumulator addressing.
See Also
External Links
- Eyes & Lichty, page 524 on XBA
- Labiak, page 204 on XBA
- snes9x implementation of XBA: https://github.com/snes9xgit/snes9x/blob/master/cpuops.cpp#L3261
- undisbeliever on XBA: https://undisbeliever.net/snesdev/65816-opcodes.html#xba-exchange-the-b-and-a-accumulators
- Clark, Bruce. http://www.6502.org/tutorials/65c816opcodes.html#6.10.3