We've just updated MediaWiki and its underlying software. If anything doesn't look or work quite right, please mention it to us. --RanAS
RGB Encoder: Difference between revisions
From SnesLab
(→References: bullet points -> number) |
(superscripted 1) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Video Encoder schematic.png|thumb|The RGB Encoder (aka Video Encoder), straddling regions B4 and B5 of the [[jwdonal schematic]]]] | [[File:Video Encoder schematic.png|thumb|The RGB Encoder (aka Video Encoder), straddling regions B4 and B5 of the [[jwdonal schematic]]]] | ||
The '''RGB Encoder''', as it is called in the official Super Nintendo development manual [1], converts analog RGB signals (pins 20, 21, and 22) from the [[Darlington triad]] to composite video output for [[Multi-Out]]. It also outputs to the [[RF Modulator]]. | The '''RGB Encoder''', as it is called in the official Super Nintendo development manual <sup>[1]</sup>, converts analog RGB signals (pins 20, 21, and 22) from the [[Darlington triad]] to composite video output for [[Multi-Out]]. It also outputs to the [[RF Modulator]]. | ||
=== References === | === References === | ||
Latest revision as of 00:32, 15 July 2023
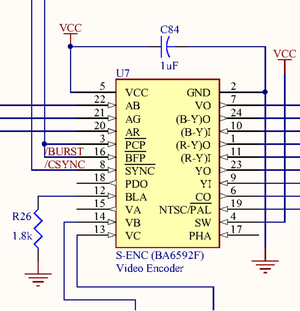
The RGB Encoder (aka Video Encoder), straddling regions B4 and B5 of the jwdonal schematic
The RGB Encoder, as it is called in the official Super Nintendo development manual [1], converts analog RGB signals (pins 20, 21, and 22) from the Darlington triad to composite video output for Multi-Out. It also outputs to the RF Modulator.
References
- Figure 2-22-1, "Super NES Functional Block Diagram" on page 2-22-2 of Book I of the official Super Nintendo development manual
- http://problemkaputt.de/fullsnes.htm#snespinoutsmiscchips
- https://wiki.console5.com/tw/images/e/e6/BA6592F.pdf

