We've just updated MediaWiki and its underlying software. If anything doesn't look or work quite right, please mention it to us. --RanAS
GETB (Super FX): Difference between revisions
From SnesLab
(Z) |
(The ALT0 state is restored.) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
R<sub>14</sub> serves as the ROM address pointer. | R<sub>14</sub> serves as the ROM address pointer. | ||
The reason the cycle times can vary is because of the [[ROM buffer]]. | The reason the cycle times can vary is because of the [[ROM buffer]]. The [[ALT0]] state is restored. | ||
The destination register should be specified in advance using [[WITH]] or [[TO]]. Otherwise, R<sub>0</sub> serves as the default. | The destination register should be specified in advance using [[WITH]] or [[TO]]. Otherwise, R<sub>0</sub> serves as the default. | ||
Revision as of 00:06, 13 July 2024
| Basic Info | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Addressing Mode | Opcode | Length | ROM Speed | RAM Speed | Cache Speed | ||
| Implied (type 1) | EF | 1 byte | 3 to 8 cycles | 3 to 9 cycles | 1 to 6 cycles | ||
| Flags Affected | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | ALT1 | ALT2 | O/V | S | CY | Z | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | . | . | . | . | ||
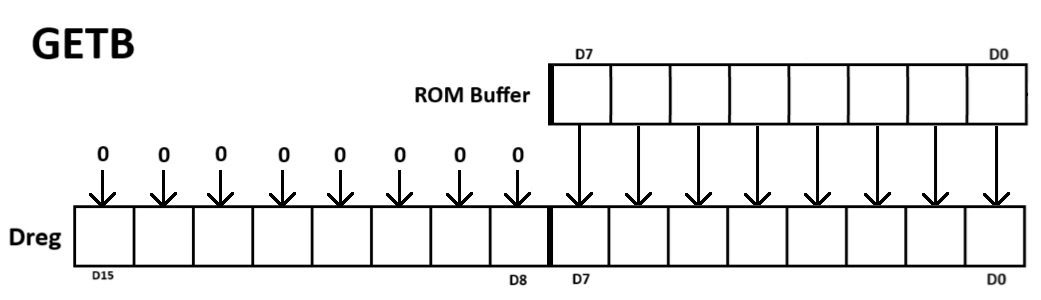
GETB (Get Byte) is a Super FX instruction that loads one byte from the ROM buffer into the low byte of the destination register. The high byte of the destination register is zeroed.
R14 serves as the ROM address pointer.
The reason the cycle times can vary is because of the ROM buffer. The ALT0 state is restored.
The destination register should be specified in advance using WITH or TO. Otherwise, R0 serves as the default.
Syntax
GETB
Example
Let:
ROM buffer = 0075h Dreg : R0
After executing GETB:
R0 = 0075h
See Also
External Links
- Official Super Nintendo development manual on GETB: 9.35 on Page 2-9-49 of Book II
- example: page 2-9-50 of Book II, lbid