S-DSP/Noise: Difference between revisions
(added categories) |
(linkify FLG) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
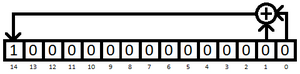
Hardware noise on the SNES is generated by a 15-bit Fibonacci [https://www.eetimes.com/tutorial-linear-feedback-shift-registers-lfsrs-part-1/ linear-feedback shift register]. <sup>[1]</sup> Unlike the NES which has two hardware noise timbres, the SNES only has one. The taps are located at bits 0 & 1, which are XOR'd together and fed back into bit 14 while the whole register shifts to the right (dividing everything else by two). <sup>[2]</sup> Its initial seed value is 4000h and its period is 32,767 (2^15 - 1), after which the noise audibly repeats. [[S-DSP/Noise/Values|See all of the values here.]] | Hardware noise on the SNES is generated by a 15-bit Fibonacci [https://www.eetimes.com/tutorial-linear-feedback-shift-registers-lfsrs-part-1/ linear-feedback shift register]. <sup>[1]</sup> Unlike the NES which has two hardware noise timbres, the SNES only has one. The taps are located at bits 0 & 1, which are XOR'd together and fed back into bit 14 while the whole register shifts to the right (dividing everything else by two). <sup>[2]</sup> Its initial seed value is 4000h and its period is 32,767 (2^15 - 1), after which the noise audibly repeats. [[S-DSP/Noise/Values|See all of the values here.]] | ||
Note that the noise sampling frequency is the perceived pitch (due to overtones) even though it is double ([https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/Nyquist-Theorem Nyquist]) that of the fundamental. It is selected via bits 0 to 4 of the FLG register in [[DSPRAM]] (see the table below). On reset, the noise frequency is reset to zero. | Note that the noise sampling frequency is the perceived pitch (due to overtones) even though it is double ([https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/Nyquist-Theorem Nyquist]) that of the fundamental. It is selected via bits 0 to 4 of the [[FLG]] register in [[DSPRAM]] (see the table below). On reset, the noise frequency is reset to zero. | ||
The [[S-DSP/Gaussian Filter|Gaussian interpolator]] does not operate on the hardware noise generator. | The [[S-DSP/Gaussian Filter|Gaussian interpolator]] does not operate on the hardware noise generator. | ||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
=== See Also === | === See Also === | ||
* [[The Infamous Bit-Of-Confusion]] | * [[The Infamous Bit-Of-Confusion]] | ||
* [[Polynomial Counter]] | |||
=== References === | === References === | ||
# https://github.com/ares-emulator/ares/blob/master/ares/sfc/dsp/dsp.hpp#L76 | # https://github.com/ares-emulator/ares/blob/master/ares/sfc/dsp/dsp.hpp#L76 | ||
# https://github.com/ares-emulator/ares/blob/master/ares/sfc/dsp/misc.cpp#L26 | # https://github.com/ares-emulator/ares/blob/master/ares/sfc/dsp/misc.cpp#L26 | ||
# [https://archive.org/details/SNESDevManual/book1/page/n174 page 3-7-8] of the official Super Nintendo development manual | # Table 3-7-4 on [https://archive.org/details/SNESDevManual/book1/page/n174 page 3-7-8] of the official Super Nintendo development manual | ||
[[Category:Audio]] | [[Category:Audio]] | ||
[[Category:SNES Hardware]] | [[Category:SNES Hardware]] | ||
[[Category:Registers]] | [[Category:Registers]] | ||
Latest revision as of 08:45, 1 December 2023
Noise clock table
Hardware noise on the SNES is generated by a 15-bit Fibonacci linear-feedback shift register. [1] Unlike the NES which has two hardware noise timbres, the SNES only has one. The taps are located at bits 0 & 1, which are XOR'd together and fed back into bit 14 while the whole register shifts to the right (dividing everything else by two). [2] Its initial seed value is 4000h and its period is 32,767 (2^15 - 1), after which the noise audibly repeats. See all of the values here.
Note that the noise sampling frequency is the perceived pitch (due to overtones) even though it is double (Nyquist) that of the fundamental. It is selected via bits 0 to 4 of the FLG register in DSPRAM (see the table below). On reset, the noise frequency is reset to zero.
The Gaussian interpolator does not operate on the hardware noise generator.
| FLG.0-4 | Sampling Frequency | Pitch | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | 0 Hz | off | |
| 01 | 16 Hz | C0 - 38¢ | |
| 02 | 21 Hz | E0 + 33¢ | |
| 03 | 25 Hz | G0 + 35¢ | |
| 04 | 31 Hz | B0 + 7¢ | |
| 05 | 42 Hz | E1 + 33¢ | |
| 06 | 50 Hz | G1 + 35¢ | |
| 07 | 63 Hz | B1 + 35¢ | |
| 08 | 83 Hz | E2 + 12¢ | |
| 09 | 100 Hz | G2 + 35¢ | |
| 0A | 125 Hz | B2 + 21¢ | |
| 0B | 167 Hz | E3 + 23¢ | |
| 0C | 200 Hz | G3 + 35¢ | |
| 0D | 250 Hz | B3 + 21¢ | |
| 0E | 333 Hz | E4 + 18¢ | |
| 0F | 400 Hz | G4 + 35¢ | |
| 10 | 500 Hz | B4 + 21¢ | |
| 11 | 667 Hz | E5 + 20¢ | |
| 12 | 800 Hz | G5 + 35¢ | |
| 13 | 1.0 kHz | B5 + 21¢ | |
| 14 | 1.3 kHz | E6 - 24¢ | |
| 15 | 1.6 kHz | G6 + 35¢ | |
| 16 | 2.0 kHz | B6 + 21¢ | |
| 17 | 2.7 kHz | E7 + 41¢ | |
| 18 | 3.2 kHz | G7 + 35¢ | |
| 19 | 4.0 kHz | B7 + 21¢ | |
| 1A | 5.3 kHz | E8 + 9¢ | |
| 1B | 6.4 kHz | G8 + 35¢ | |
| 1C | 8.0 kHz | B8 + 21¢ | |
| 1D | 10.7 kHz | E9 + 25¢ | |
| 1E | 16 kHz | B9 + 21¢ | |
| 1F | 32 kHz | B10 + 21¢ |
See Also
References
- https://github.com/ares-emulator/ares/blob/master/ares/sfc/dsp/dsp.hpp#L76
- https://github.com/ares-emulator/ares/blob/master/ares/sfc/dsp/misc.cpp#L26
- Table 3-7-4 on page 3-7-8 of the official Super Nintendo development manual